44 who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant?
Sociology of Deviant Behavior - Flashcards | StudyHippo.com Click card to see the answer. answer. examining the reactions of others to behavior. Join StudyHippo to unlock the other answers. Join Studyhippo. question. Jeffery has been labeled deviant by family, friends an the criminal justice system. He joins a deviant subculture and others see him in the deviant roles. Sociology: Unit 5 Flashcards | Quizlet Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant? Howard Becker In Merton's strain theory, which of the following means accepting the goal but using unacceptable, or deviant, ways of reaching this goal? Innovation Who serves as a primary connection between the population and the criminal justice system? Police
Top 100 Deviant Behavior Examples - Tutorsploit Bribery is the deviant behavior of an individual offering money, perks, or special favors to another person in a position of power. Bribing is done to influence people. 17. Drug abuse Drug abuse refers to the illegal or improper use of drugs. Drug abusers become addicts, and their lives are controlled by using more and more drugs. 18. Vagrancy
Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant?
Unit 5: Deviance & Crime Flashcards | Quizlet Howard Becker Argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant. Stigmas Are very powerful negative labels that change a person's identity. Robert Merton Argued that when this happened that it was generally because of how society was organized. Strain Theory Printable Flash Cards Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant? Howard Becker -According to Durkheim, deviance can lead to social change in society. ... Conflict theorists argue that social stratification often leads to conflict and other negative consequences because some people have more than others. The Role of Adaptive Behavior Assessment - NCBI Bookshelf Adaptive behavior has been an integral, although sometimes unstated, part of the long history of mental retardation and its definition. In the 19th century, mental retardation was recognized principally in terms of a number of factors that included awareness and understanding of surroundings, ability to engage in regular economic and social life, dependence on others, the ability to maintain ...
Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant?. 5.10 : Deviance and Crime Flashcards | Quizlet Most sociologists accept biological explanations for deviance as the best possible explanations false Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant? Howard Becker Merton argued that some individuals may choose to identify new goals and new means to reach them, which is known as conformity false Sociological Theories of Crime | National University Labeling Theory argues that deviant behavior is often a consequence of having a deviant-like label applied to a person. For example, a teacher labeling a student as a troublemaker. That label can then be mentally adopted by the person it's been assigned to, leading them to exhibit the actions, attitudes, and behaviors associated with it. What Does Howard Becker Call Individuals Who Specifically Choose To ... When sociologists use the term deviant? Sociologists use the term deviance to refer to a violation of norms. 1. According to sociologist Howard S. Becker it is not the act itself that makes an action deviant but rather how society reacts to it. Theories of Deviance - CliffsNotes A type of symbolic interaction, labeling theory concerns the meanings people derive from one another's labels, symbols, actions, and reactions. This theory holds that behaviors are deviant only when society labels them as deviant.
Deviant Behavior - Definition, Examples, Cases, Processes Dr. Mendel explained that Alegria's deviant behavior stemmed from the convergence of violent and sexual images in his mind when he was young. In this example of deviant behavior, the murderer had developed an unnatural view of society's acceptance of both sexual acts and extreme violence. Related Legal Terms and Issues How Psychology Defines and Explains Deviant Behavior - ThoughtCo First, the individual is the primary unit of analysis. This means that psychologists believe that individual human beings are solely responsible for their criminal or deviant acts. Second, an individual's personality is the major motivational element that drives behavior within individuals. Chapter 7. Deviance, Crime, and Social Control – Introduction ... The deviant is one to whom the label has successfully been applied; deviant behaviour is behaviour people so label” (1963). It is important to note that labelling theory does not address the initial motives or reasons for the rule-breaking behaviour, which might be unknowable, but the importance of its social consequences. Labeling Theory | Howard Becker | Definition, Examples ... Oct 08, 2021 · When individuals have little social support from conventional society, they can turn to deviant groups, where having a deviant label is accepted. However, this can create rationalization, attitudes, and opportunities that make involvement in these groups a risk factor for further deviant behavior (Bernburg, Krohn, and Rivera, 2006).
Chapter 10: Friendship Relationships – Interpersonal ... Deviant Friendship. The final category of friendships we may have is deviant friendships, more commonly referred to as toxic friendships. For our purposes here, we use the term “deviant” because it refers to any behavior that violates behavioral norms. Deviant Behavior: Definition, Causes, and Types - Verywell Mind There are a variety of theories that explain why people engage in deviant behavior, including psychological, biological, and sociological explanations. In reality, there are likely many factors that play a role in deviant behavior. These include genetics, personality, upbringing, environment, and societal influences. Sociology: Unit 5- Deviance and crime Flashcards | Quizlet a sociologist who argued that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant Conformity Merton defined this as a meaning that the person accepted the cultural goal and used acceptable ways of trying to reach this goal Control theory Identifies 4 different types of social control that keep people conforming to society's norms. PDF CHAPTER ONE: WHAT IS DEVIANT BEHAVIOR? Multiple Choice Questions c) to make moral judgments about deviant behavior. d) to study biases toward persons seen as deviant. Difficulty: 1 Page Reference: 6-7 Answer: b) seeking out the causes of deviant behavior. 25. All of the following are assumptions of the constructionist perspective on deviance, EXCEPT that deviance should be seen as a) a label. b) an objective ...
THE CRIMINAL PSYCHOPATH: HISTORY, NEUROSCIENCE, TREATMENT ... The 20 Items Listed on the Psychopathy Checklist-Revised (Hare 1991; 2003) The items corresponding to the early two-factor conceptualization of psychopathy, 89 subsequent three-factor model, 90 and current four-factor model are listed. 91 The two-factor model labels are Interpersonal-Affective (Factor 1) and Social Deviance (Factor 2); the three-factor model labels are Arrogant and Deceitful ...
7.2 Explaining Deviance - Sociology - University of Minnesota Travis Hirschi (1969) argued that human nature is basically selfish and thus wondered why people do not commit deviance. His answer, which is now called social control theory (also known as social bonding theory ), was that their bonds to conventional social institutions such as the family and the school keep them from violating social norms.
Role theory - Wikipedia Social sanctions (punishment and reward) are used to influence role behavior. These three aspects are used to evaluate one's own behavior as well as the behavior of other people. Heinrich Popitz defines social roles as norms of behavior that a special social group has to follow. Norms of behavior are a set of behaviors that have become typical ...
Deviance and Crime: How Sociologists Study Them - ThoughtCo Structural strain theory was developed by American sociologist Robert K. Merton and suggests that deviant behavior is the result of strain an individual may experience when the community or society in which they live does not provide the necessary means to achieve culturally valued goals.
What Does Howard Becker Call Individuals Who Specifically Choose To ... Howard Becker argued that the deviant label can become a 'master status' in which the individual's deviant identity overrules all other identities. Becker argues that there are 5 stages in this process: The Individual is publicly labelled as a deviant which may lead to rejection from several social groups. What is individual deviance?
Deviance (sociology) - Wikipedia Deviance or the sociology of deviance explores the actions and/or behaviors that violate social norms across formally enacted rules (e.g., crime) as well as informal violations of social norms (e.g., rejecting folkways and mores).Although deviance may have a negative connotation, the violation of social norms is not always a negative action; positive deviation exists in some situations.
Thio TB Ch1 - answer bank - CHAPTER ONE What Is Deviant Behavior ... b) lawmakers and law enforcers. c) nondeviants who label others deviants rather than deviant behavior and persons. d) deviant behavior and persons rather than nondeviants who label others deviants. Answer: D; Page Reference: 6; Bloom's Category: Remembering. Early in the twentieth century, criminologists believed that a) criminals are made ...
What is Deviant Behavior? - Study.com Emile Durkheim, a French sociologist, theorized that deviant behavior is both unavoidable and necessary in order for society to properly function as a whole. His ideas were referenced as the...
Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label ... Explanation: Howard Saul Becker a sociologist who has made significant achievements to the sociology of deviance, sociology of art, and sociology of music. He is the one who have said that "social groups create deviance by making the rules whose infraction constitutes deviance". Advertisement Answer 17 people found it helpful Brainly User
Sociology Unit 5 Notes.docx - Sociology Unit 5: Deviance... Sociology Unit 5: Deviance and Crime Deviance-the violation of a culture's norms. Labeling Theory-deviance occurs not because of what people do but how people respond to those actions Howard Becker-argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant. In other words, it is the response to a behavior that makes it deviant and not the behavior itself. Stigmas- very ...
Social stigma - Wikipedia The physically disabled, mentally ill, homosexuals, and a host of others who is labeled deviant because they deviate from the expectations of a group, are subject to stigmatization-the social rejection of numerous individuals, and often entire groups of people who have been labeled deviant. [full citation needed] Stigma communication
Test #1 Study Guide (Deviant Behavior) Flashcards | Quizlet The sociological concept of deviance was. unknown before the 1950s. Scholars studying deviance are interested in. what makes the behavior deviant, the nature of the deviant act, how one comes to commit deviant acts, and the consequences of committing deviant acts. The _____ definition of deviance asserts that deviance is in the eye of the beholder.
Deviant Behavior - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Sociology and psychiatry have a common topic: deviant behavior. Sociology, as a scientific discipline which examines the rules by which society functions, must have a genuine interest in phenomena which threaten these rules. Emile Durkheim (1895 ), one of the founding fathers of sociology, points out in his famous book, The Rules of the ...
The Labelling Theory of Crime - ReviseSociology Howard Becker argued that the deviant label can become a 'master status' in which the individual's deviant identity overrules all other identities. Becker argues that there are 5 stages in this process: The Individual is publicly labelled as a deviant, which may lead to rejection from several social groups.
Sociology Flashcards Symbolic interactionism argues that the social world is created through every day interactions and shared meanings. Definition. True: ... Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant? Definition. Howard Becker: Term. According to Durkheim, deviance can lead to social change in society. Definition. True:
The Role of Adaptive Behavior Assessment - NCBI Bookshelf Adaptive behavior has been an integral, although sometimes unstated, part of the long history of mental retardation and its definition. In the 19th century, mental retardation was recognized principally in terms of a number of factors that included awareness and understanding of surroundings, ability to engage in regular economic and social life, dependence on others, the ability to maintain ...
Printable Flash Cards Who argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant? Howard Becker -According to Durkheim, deviance can lead to social change in society. ... Conflict theorists argue that social stratification often leads to conflict and other negative consequences because some people have more than others.
Unit 5: Deviance & Crime Flashcards | Quizlet Howard Becker Argues that deviant behavior is only deviant because people label it as deviant. Stigmas Are very powerful negative labels that change a person's identity. Robert Merton Argued that when this happened that it was generally because of how society was organized. Strain Theory

![PDF] Causes and Consequence Deviant Workplace Behavior ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/bd0f2220fa4d7fe46579ab0fa538daeb20ccecda/2-Figure1-1.png)
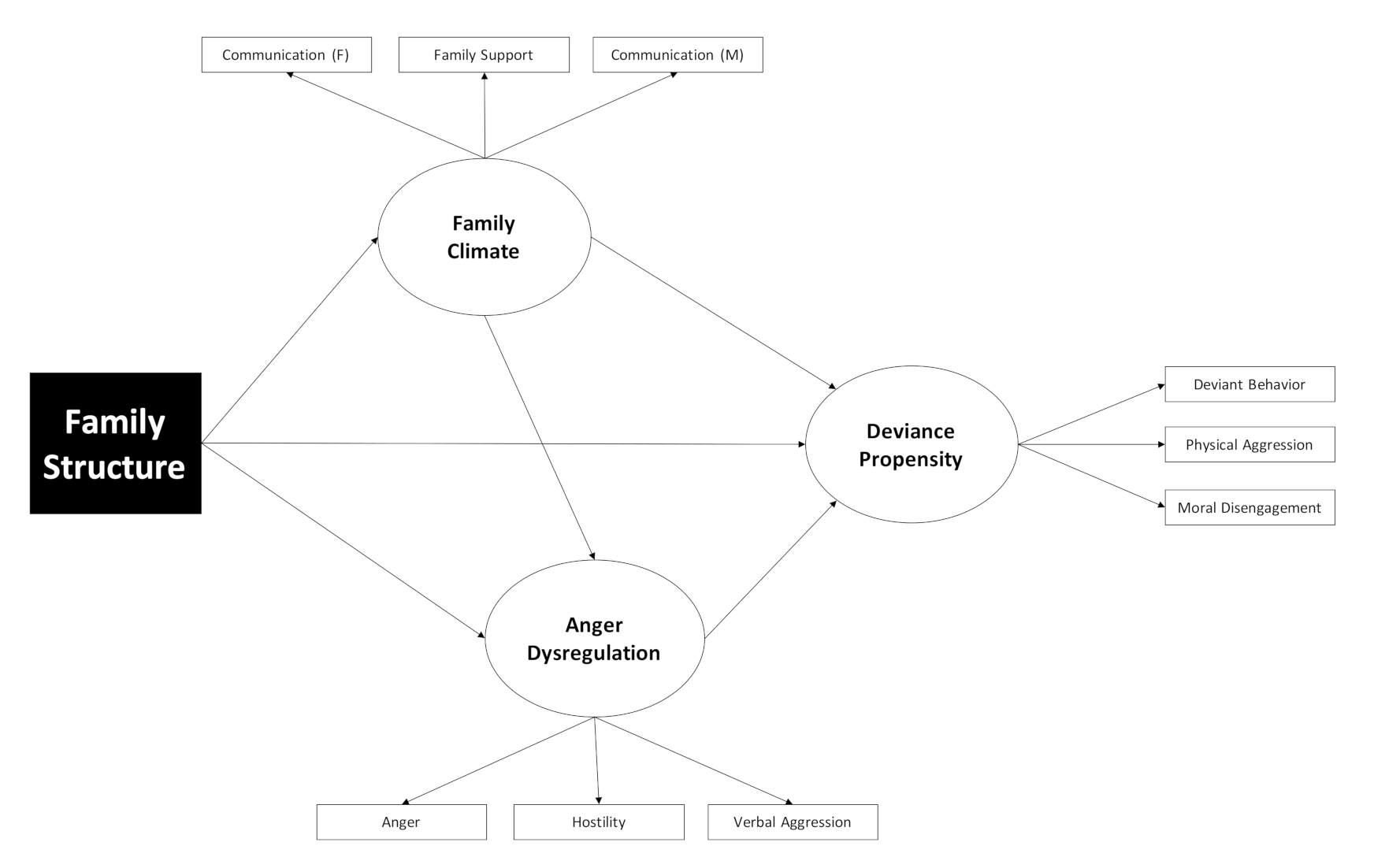















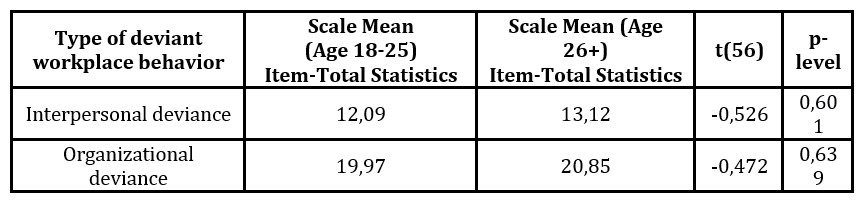


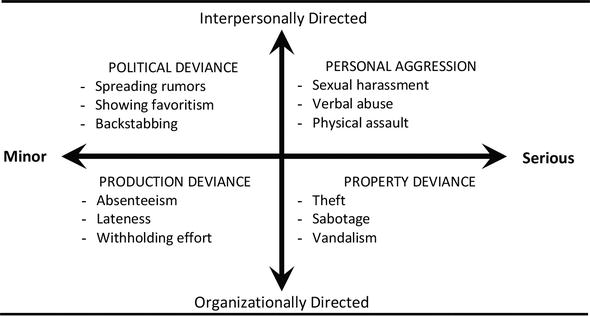
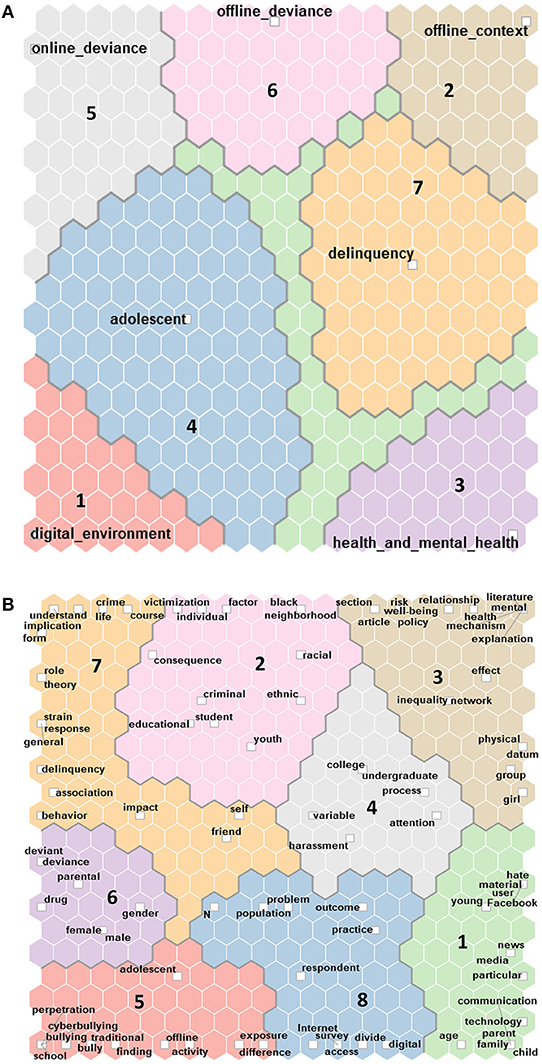








Komentar
Posting Komentar